Business Model Canvas for Digital Businesses
This article will cover the popular Business Model Canvas (BMC) tool from the perspective of digital business models.
The BMC is aiming to be relevant for all types of business models, including non-tech, commodities, consumer packaged goods, insurance, mining and anything else.
We on the other hand only care about digital businesses like Google, Meta/Facebook, Uber, Airbnb, Amazon, Netflix, etc.
With this laser-focus we are able to provide far more value when it comes to types and examples for each of the sections of the BMC. That’s the aim of this article!
Note also that we have a separate article to each part of the BMC tailored to digital biz models.
The Business Model Canvas was devised by Alex Osterwalder
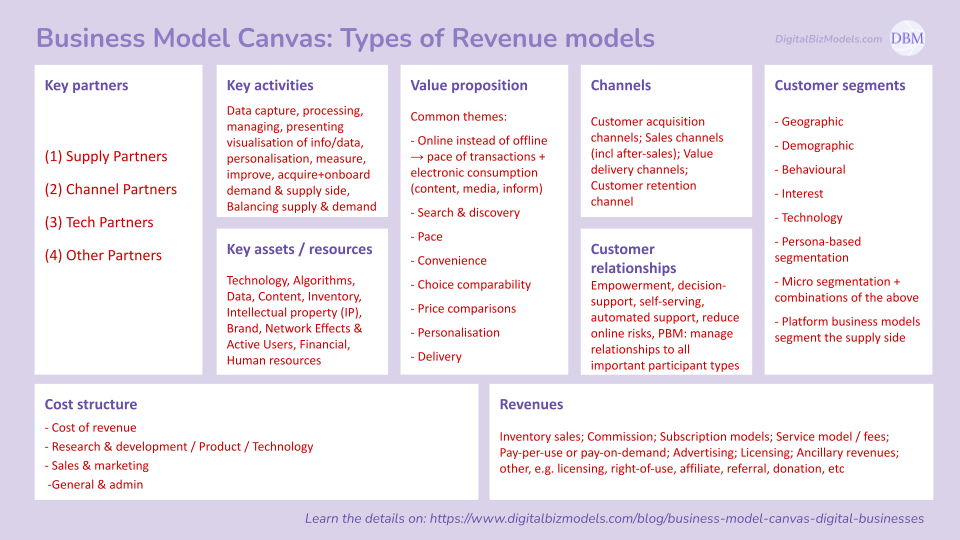
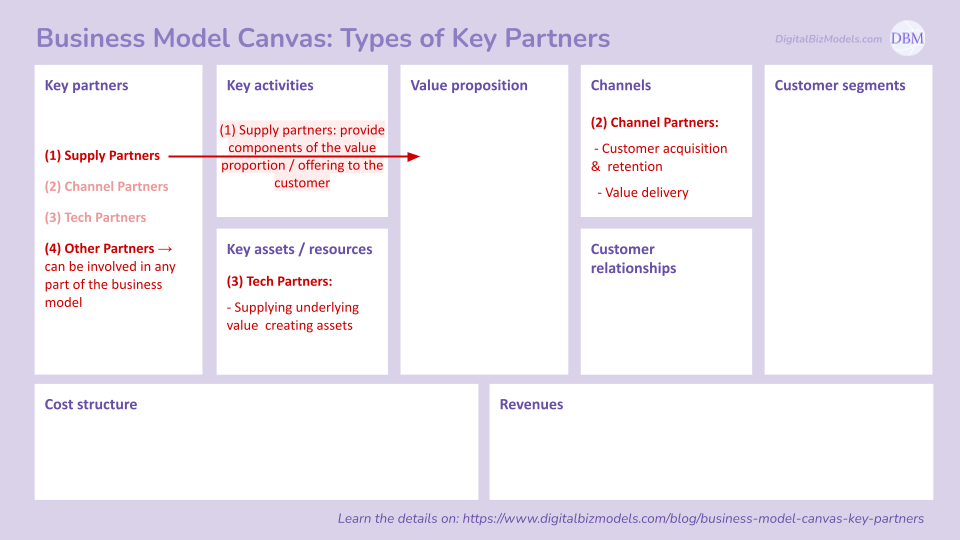
(1) Key Partners
Here we can distinguish between:
Supply Partners from which the key inputs get sourced. It is important to note the significant differences among vertical-specific supply partners which is why we are providing an extensive list of examples in this article
Channel Partners can be involved in customer acquisition, retention and value delivery
Tech Partners providing components of the key value creating assets
Other Partners for all sorts of aspects of the business model, e.g. investors, legal, professional service and many more
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Key Partners in Digital Business Models.
Course
Digital Business Models
11 Verticals of Disruption
The only online course that systematically covers the major types of digital business models, revealing 200 Playbook Tactics and 70 Monetisation Tactics all presented in the Business Model Canvas
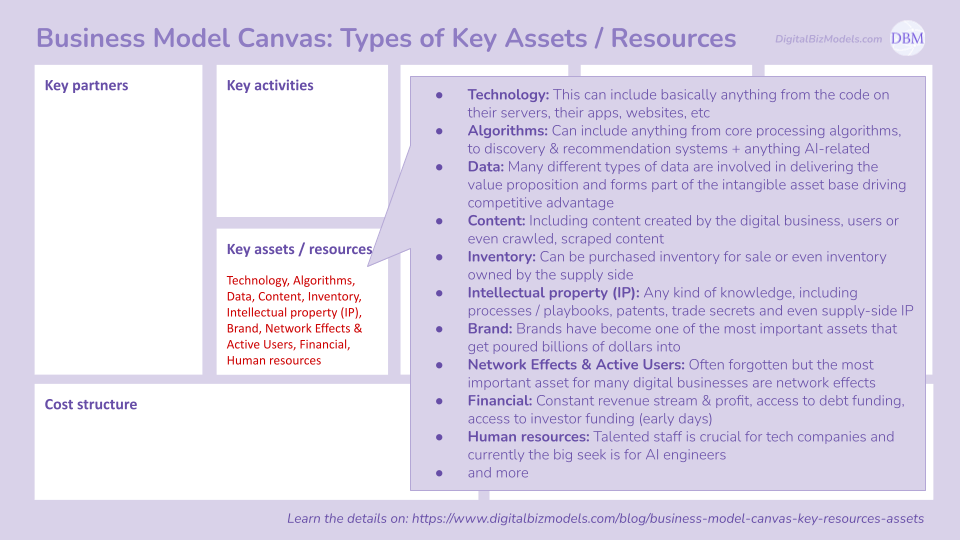
(2) Key Assets & Resources
Some of the most important Key Assets & Resources for Digital Business Models are:
Technology: This can include basically anything from the code on their servers, their apps, websites, etc
Algorithms: Can include anything from core processing algorithms, to discovery & recommendation systems + anything AI-related
Data: Many different types of data are involved in delivering the value proposition and forms part of the intangible asset base driving competitive advantage
Content: Including content created by the digital business, users or even crawled, scraped content
Inventory: Can be purchased inventory for sale or even inventory owned by the supply side
Intellectual property (IP): Any kind of knowledge, including processes / playbooks, patents, trade secrets and even supply-side IP
Brand: Brands have become one of the most important assets that get poured billions of dollars into
Network Effects & Active Users: Often forgotten but the most important asset for many digital businesses are network effects
Financial: Constant revenue stream & profit, access to debt funding, access to investor funding (early days)
Human resources: Talented staff is crucial for tech companies and currently the big seek is for AI engineers
and more
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Key Assets & Resources in Digital Business Models.
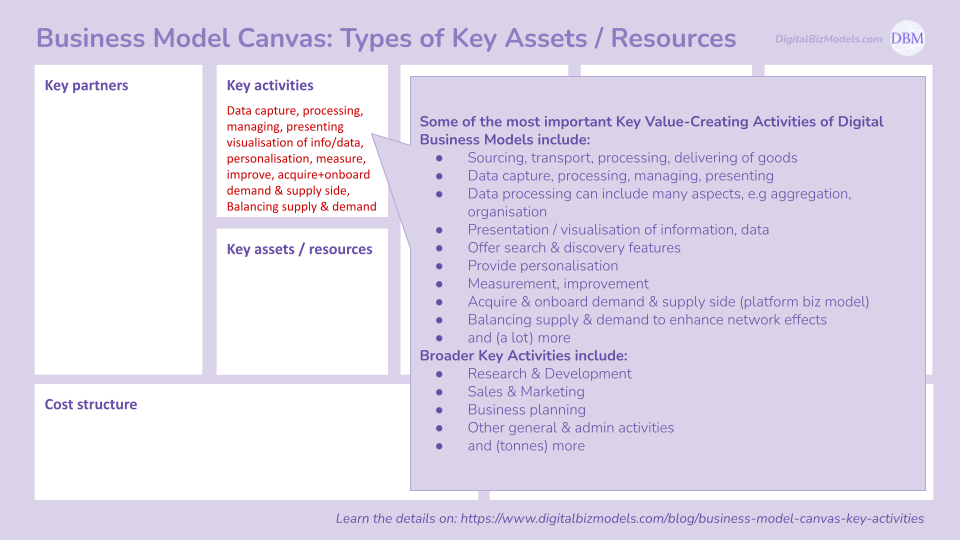
(3) Key Activities
Some of the most important Key Value-Creating Activities of Digital Business Models include:
Sourcing, transport, processing, delivering of goods
Data capture, processing, managing, presenting
Data processing can include many aspects, e.g aggregation, organisation
Presentation / visualisation of information, data
Offer search & discovery features
Provide personalisation
Measurement, improvement
Acquire & onboard demand & supply side (platform biz model)
Balancing supply & demand to enhance network effects
and (a lot) more
Broader Key Activities include:
Research & Development
Sales & Marketing
Business planning
Other general & admin activities
and (tonnes) more
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Key Activities in Digital Business Models.
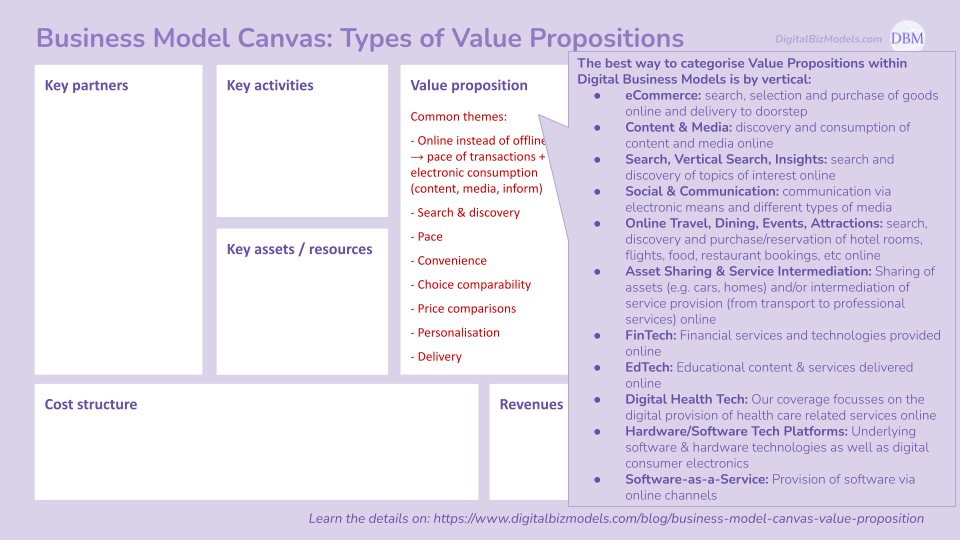
(4) Value Proposition
The best way to categorise Value Propositions within Digital Business Models is by vertical:
eCommerce: search, selection and purchase of goods online and delivery to doorstep
Content & Media: discovery and consumption of content and media online
Search, Vertical Search, Insights: search and discovery of topics of interest online
Social & Communication: communication via electronic means and different types of media
Online Travel, Dining, Events, Attractions: search, discovery and purchase/reservation of hotel rooms, flights, food, restaurant bookings, etc online
Asset Sharing & Service Intermediation: Sharing of assets (e.g. cars, homes) and/or intermediation of service provision (from transport to professional services) online
FinTech: Financial services and technologies provided online
EdTech: Educational content & services delivered online
Digital Health Tech: Our coverage focusses on the digital provision of health care related services online
Hardware/Software Tech Platforms: Underlying software & hardware technologies as well as digital consumer electronics
Software-as-a-Service: Provision of software via online channels
That said, there a number of common themes though we encourage never to look at generic lists and be more specific like in the list above:
Online instead of offline → pace of transactions + electronic consumption (content, media, inform)
Search & discovery
Pace
Convenience
Choice comparability
Price comparisons
Personalisation
Delivery
Note that in this list we have been focussing on the main end-consumer-facing value propositions. In each of these verticals there can be additional supply, backend and intermediary value propositions that dont interact with the end consumer.
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Value Propositions in Digital Business Models.
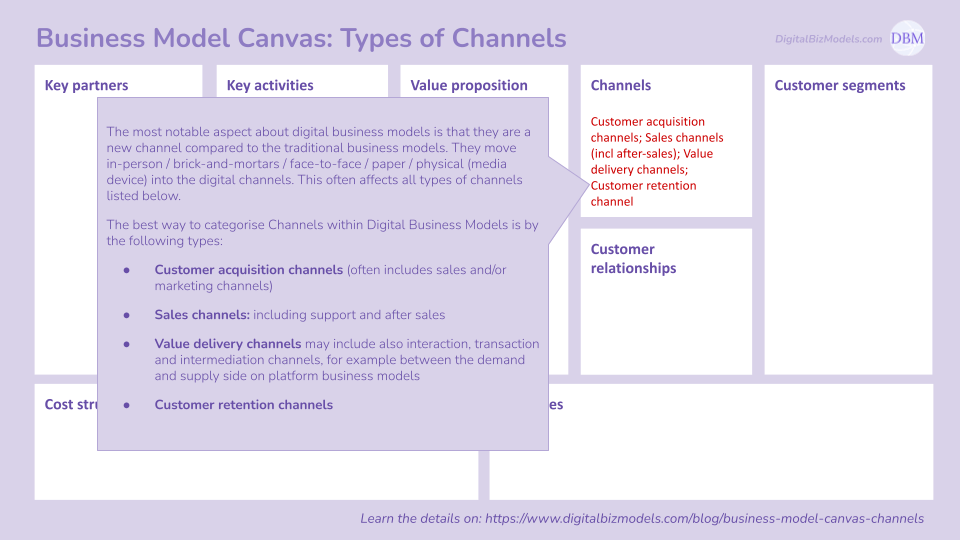
(5) Channels
The most notable aspect about digital business models is that they are a new channel compared to the traditional business models. They move in-person / brick-and-mortars / face-to-face / paper / physical (media device) into the digital channels. This often affects all types of channels listed below.
The best way to categorise Channels within Digital Business Models is by the following types:
Customer acquisition channels (often includes sales and/or marketing channels)
Sales channels: including support and after sales
Value delivery channels may include also interaction, transaction and intermediation channels, for example between the demand and supply side on platform business models
Customer retention channels
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Channels in Digital Business Models.
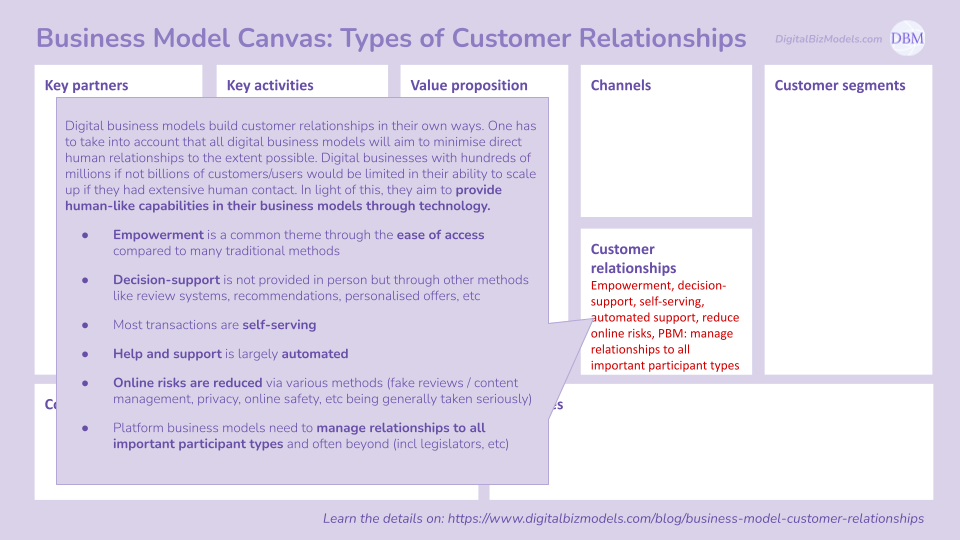
(6) Customer Relationships
Digital business models build customer relationships in their own ways. One has to take into account that all digital business models will aim to minimise direct human relationships to the extent possible. Digital businesses with hundreds of millions if not billions of customers/users would be limited in their ability to scale up if they had extensive human contact. In light of this, they aim to provide human-like capabilities in their business models through technology.
The best way to understand Customer Relationships within Digital Business Models is through the following types:
Empowerment is a common theme through the ease of access compared to many traditional methods
Decision-support is not provided in person but through other methods like review systems, recommendations, personalised offers, etc
Most transactions are self-serving
Help and support is largely automated
Online risks are reduced via various methods (fake reviews / content management, privacy, online safety, etc being generally taken seriously)
Platform business models need to manage relationships to all important participant types and often beyond (incl legislators, etc)
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Customer Relationships in Digital Business Models.
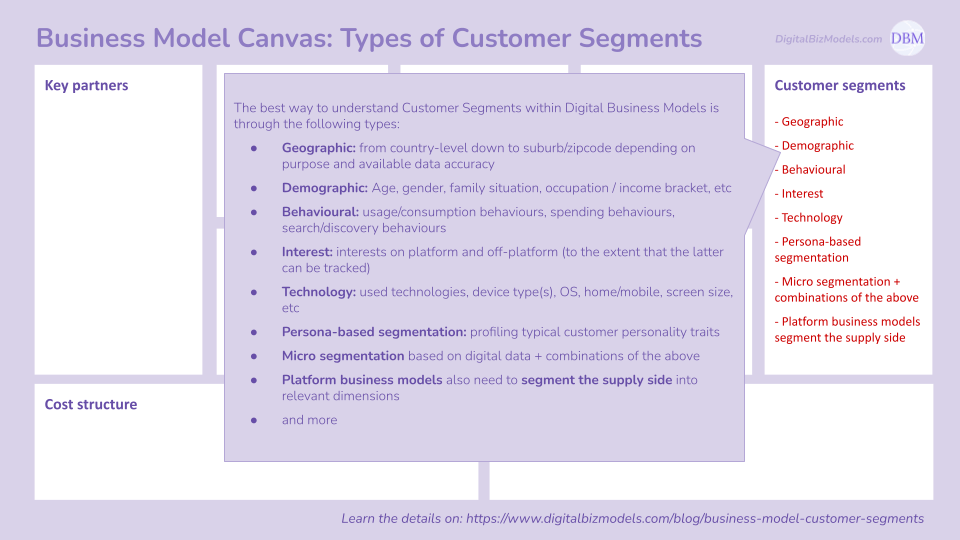
(7) Customer Segments
The best way to understand Customer Segments within Digital Business Models is through the following types:
Geographic: from country-level down to suburb/zipcode depending on purpose and available data accuracy
Demographic: Age, gender, family situation, occupation / income bracket, etc
Behavioural: usage/consumption behaviours, spending behaviours, search/discovery behaviours
Interest: interests on platform and off-platform (to the extent that the latter can be tracked)
Technology: used technologies, device type(s), OS, home/mobile, screen size, etc
Persona-based segmentation: profiling typical customer personality traits
Micro segmentation based on digital data + combinations of the above
Platform business models also need to segment the supply side into relevant dimensions
and more
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Customer Relationships in Digital Business Models.
(8) Cost Structure
Typical Cost Structures of Digital Business Models look like the below:
Cost of revenue:
Cost of goods sold
Cost of hosting and operating their IT technology, incl operations staff
Various types of depreciation expenses
Customer support & customer experience (for paying customers)
Research & development / Product / Technology:
maintaining and
enhancing existing functionality
+ adding new functionality
Sales & marketing:
Personnel cost for sales, sales support, business development, marketing, brand building, media, corporate communications
Customer support & customer experience cost for non-paying customers/users
Brand and performance advertising
General & admin:
Costs of overhead functions
Stock-based compensation for the senior executives
3rd party services, e.g. audit, legal, recruiting services, etc
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Cost Structure in Digital Business Models.
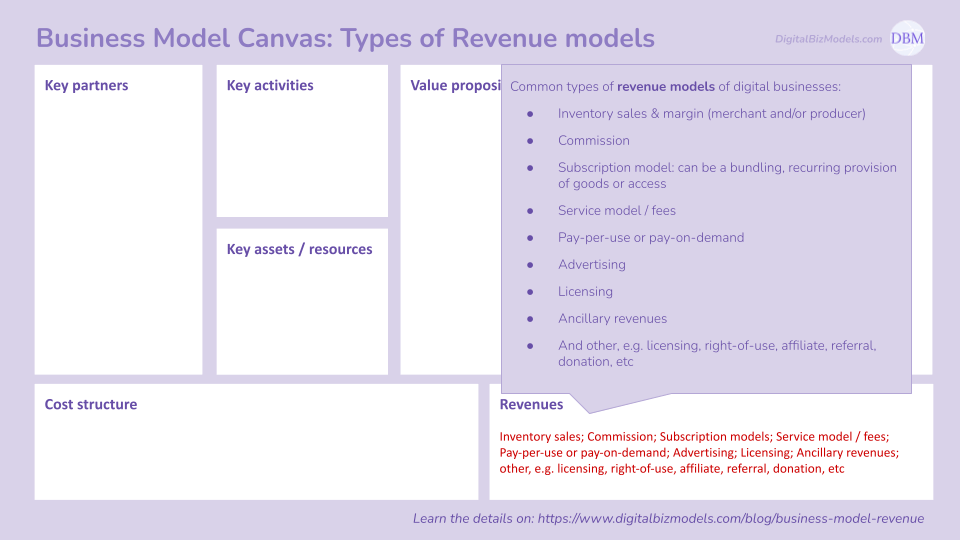
(9) Revenue generation
Typical Revenue generation of Digital Business Models look like the below:
Inventory sales & margin (merchant and/or producer)
Commission
Subscription model: can be a bundling, recurring provision of goods or access
Service model / fees
Pay-per-use or pay-on-demand
Advertising
Licensing
Ancillary revenues
And other, e.g. licensing, right-of-use, affiliate, referral, donation, etc
Check out for more details, examples & a summary image in the dedicated article on Revenues in Digital Business Models.